5G Core: Understanding the Foundation of Next-Generation Networks
telcomatraining.com – The rollout of 5G is transforming the telecommunications landscape, enabling faster connectivity, ultra-low latency, and support for billions of devices worldwide. At the heart of this transformation lies the 5G Core (5GC), the foundation of next-generation networks. Unlike previous generations, the 5G Core is not just an upgrade; it is a complete architectural redesign that supports advanced capabilities like network slicing, edge computing, and massive IoT integration.
What is the 5G Core?
The 5G Core is the central part of a 5G network responsible for managing data, connections, and services. Built on a cloud-native, service-based architecture (SBA), the 5GC allows operators to deliver flexible, scalable, and efficient services. Unlike the traditional 4G EPC (Evolved Packet Core), the 5G Core is designed with virtualization and containerization in mind, ensuring seamless integration with cloud and edge platforms.
In simpler terms, the 5G Core acts as the “brain” of the network, coordinating everything from device authentication to traffic routing and quality of service management.
Key Features of the 5G Core
- Service-Based Architecture (SBA): The 5GC uses microservices to provide modular, flexible functions. Each service can be independently scaled and upgraded.
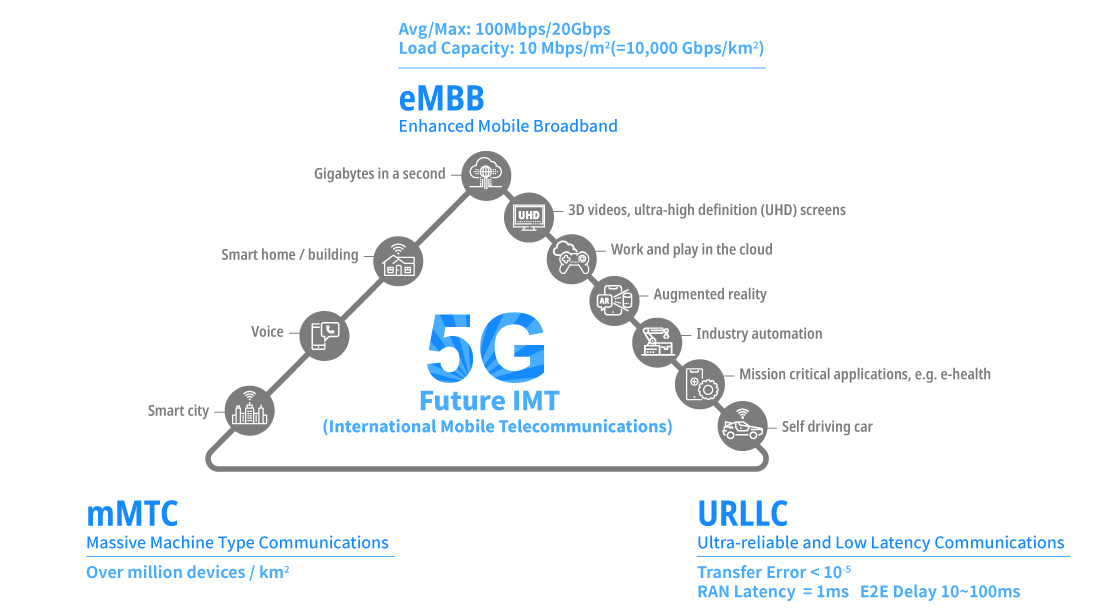
- Network Slicing: Operators can create multiple virtual networks on the same physical infrastructure. For example, one slice can prioritize autonomous vehicles, while another supports entertainment streaming.
- Edge Computing Integration: By placing data processing closer to the user, the 5GC reduces latency and improves real-time performance.
- Enhanced Security: With features like unified authentication and improved encryption, the 5G Core ensures a more secure ecosystem.
- Support for Massive IoT: The 5GC is optimized to handle millions of low-power IoT devices efficiently.
Why the 5G Core is Essential for Next-Generation Networks
The 5G Core is not just about speed—it’s about enabling new possibilities. Ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) allows industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation to adopt automation and remote control solutions. Massive machine-type communication (mMTC) supports smart cities, where sensors and devices constantly exchange data. Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) ensures users enjoy seamless video streaming, VR/AR experiences, and cloud gaming.
Without the 5G Core, these capabilities would not be possible. Its adaptability ensures that service providers can tailor offerings for enterprises, consumers, and governments alike.
Challenges in Deploying the 5G Core
While the benefits are clear, implementing the 5GC comes with challenges. Operators must invest in cloud infrastructure, retrain workforces, and manage interoperability with existing 4G networks. Additionally, ensuring robust security in a highly virtualized environment requires continuous innovation.
The Future of the 5G Core
As 5G adoption accelerates, the 5GC will evolve alongside advancements in AI-driven automation, open-source platforms, and 6G research. It will remain a critical enabler for industries exploring digital transformation and innovation.
Conclusion
The 5G Core represents the foundation of next-generation networks, bringing flexibility, scalability, and intelligence to telecommunications. By embracing cloud-native principles and supporting advanced capabilities, it enables everything from smart cities to immersive experiences. As businesses and consumers demand more from their networks, the 5G Core will continue to be the driving force behind the future of connectivity.